Growth is exciting, but it also creates complexity. As companies scale, what once felt manageable suddenly becomes chaotic. Tasks multiply, handoffs get messy, tools stop talking to each other, and your team becomes the glue holding everything together. This is the moment when business automation systems stop being a nice-to-have and become essential infrastructure for continued growth.
If you’re starting to feel bottlenecks, slower response times, or rising operational costs, you’re not alone. Fast-growing companies often outpace the systems that once served them well. The result is predictable: more manual work, inconsistent execution, and a constant sense that your internal operations aren’t keeping up with demand.
This guide breaks down why automation becomes necessary as your business scales, how to recognize the early warning signs, and what it takes to build scalable business systems that replace manual chaos with intelligent, automated workflows. Before you can design better systems, you need to understand the hidden costs of doing things the old way, one manual task at a time.

What Is Business Automation?
As companies scale, leaders often ask: What is business automation, really? It’s one of the most widely used terms in modern operations, but also one of the most misunderstood. At its core, business automation is the intentional design of workflows that replace manual, repetitive tasks with structured, consistent, technology-driven systems. It’s about creating an operational engine that runs predictablywithout relying on human effort to push every task forward.
Business automation isn’t about using more software. It’s about transforming how work moves through your organization, so your team can focus on high-value activities, not administrative busywork.
What Is Business Automation in Practical Terms?
In practical terms, business automation takes the day-to-day tasks your team currently performs by hand, like sending follow-up emails, assigning tasks, updating records, or tracking project progress, and turns them into repeatable workflows that run automatically.
A simple way to think about it:
- Humans handle decisions, relationships, and creativity.
- Systems handle rules, repeatable actions, and data movement.
Automation also differs from digitization.
Digitization moves a process from paper to digital tools.
Automation orchestrates that process so it operates without manual intervention.
Instead of your team remembering what to do next, the system does it for them accurately, every time.
Understanding a Business Automation Process
A business automation process follows a predictable pattern. No matter how simple or complex the workflow, it typically includes:
- A trigger that starts the automation
- A set of rules that determines what should happen
- One or more actions that run automatically
- A clear outcome, like a task being assigned or a message being sent
In real life, this looks like a seamless chain of events.
Example: a lead enters your system
- Trigger: A new lead submits a form.
- System Action: Their details are added to your CRM.
- System Action: They receive a personalized email.
- System Action: A sales task is scheduled for follow-up.
This is the essence of strong business automation processes, reducing the time between steps, eliminating manual data entry, and ensuring your team never misses critical actions.
Business Automation Processes vs Tools
Many growing companies confuse tools with systems. Tools are important, but they are components, not solutions.
A tool might automate one action, such as sending an invoice, creating a task, or sending a message.
A system, however, connects multiple tools and workflows into a coordinated sequence that supports the entire customer lifecycle or internal operation.
In other words:
- Tools = features
- Systems = outcomes
When leaders focus only on acquiring tools, their operations become fragmented. When they focus on designing business automation processes, the entire organization becomes aligned, efficient, and scalable.
The Real Benefits of Business Automation for Growing Companies
As your company scales, the pressure on your team and operations increases. This is where the benefits of business automation become transformative, not just in reducing manual work but in elevating how your business functions as a whole. Smart business automation isn’t about replacing people; it’s about amplifying their capacity so the organization can grow without adding unnecessary complexity or cost.
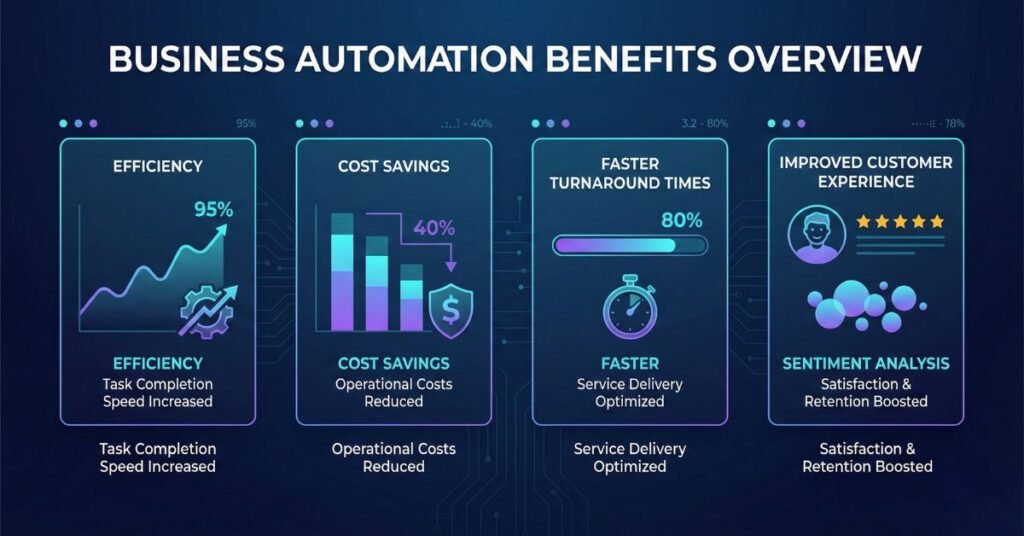
Operational Efficiency and Time Leverage
One of the most immediate benefits of automation is the dramatic reduction in repetitive, manual work. Tasks that once required hours of copying data, updating records, sending messages, or assigning follow-ups can now run automatically in the background.
The result is real-time leverage:
- Reduce manual workload by eliminating routine administrative steps.
- Faster turnaround on key processes, from onboarding to fulfillment to support.
Instead of your team acting as the operational engine, automation becomes the engine, and your people shift their focus to strategic, high-value work that drives growth.
Cost Optimization Without Increasing Headcount
As businesses grow, leaders often assume the only solution to rising workload is hiring. But more people don’t necessarily solve operational inefficiency; they can even magnify it.
Smart business automation improves productivity per employee by enabling each person to work at a higher level. They’re no longer constrained by bottlenecks, redundant tasks, or fragmented systems.
This allows you to:
- Increase output without adding payroll.
- Reallocate staff to more meaningful, revenue-driving roles.
- Scale operations sustainably instead of reactively.
Automation doesn’t replace the need for great people; it ensures every hire delivers maximum value.
Improved Customer Experience
Customer expectations continue to rise, especially around speed and personalization. Automation helps you meet those expectations consistently.
- Faster response times ensure leads are contacted quickly, and support requests never get buried.
- Personalized interactions are delivered automatically based on customer preferences, lifecycle stage, or past behavior.
When done well, automation makes your business feel more attentive, not less. Customers experience smoother onboarding, proactive communication, and timely follow-ups, all without increasing the burden on your team.
Visibility and Measurable Growth
One of the often-overlooked benefits of business automation is the clarity it brings to your operations. When workflows run consistently, data becomes far more accurate and easier to analyze.
Automation unlocks:
- Reporting dashboards that show real-time performance, not guesswork.
- Process transparency that highlights inefficiencies before they become problems.
With reliable data and consistent execution, leaders can make informed decisions, forecast more accurately, and adjust strategy with confidence. Growth becomes intentional instead of reactive.
Introducing the 4-Layer Growth Infrastructure Model™
The easiest way to approach automation strategically is through a clear, structured model that shows how scalable systems are built.
Keeping this in mind, we at Ales have designed the 4-Layer Growth Infrastructure Model™ that defines the layers of the growth process for any business.
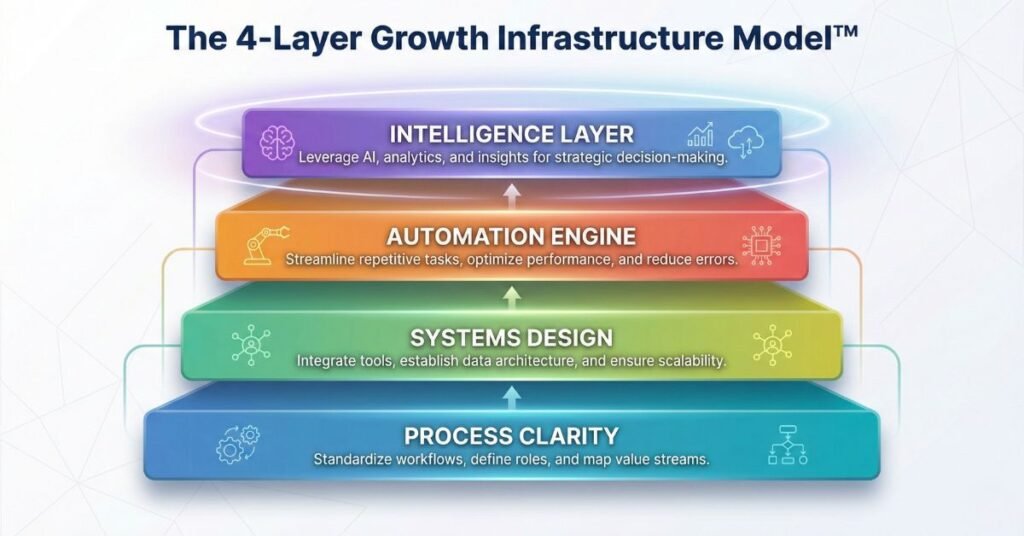
Layer 1: Process Clarity
Growth collapses without clear workflows. This layer focuses on documenting and simplifying the steps required to deliver your products, services, and internal operations.
Layer 2: Systems Design
Tools must work together, not in isolation. This layer ensures CRMs, project management systems, communication tools, and financial platforms function as one coordinated ecosystem.
Layer 3: Automation Engine
This is where structured, rule-based workflows replace manual effort, routing tasks, updating records, sending messages, and ensuring nothing falls through the cracks.
Layer 4: Intelligence Layer
AI-driven prediction, personalization, and adaptive optimization sit on top of your automation engine, enabling more responsive, data-informed operations.
This model gives companies a clear roadmap for building automation that supports long-term scalability.
How a Business Automation Workflow Actually Works
Most teams understand the automation conceptually but struggle to visualize how it actually works in the real world. A well-designed business automation workflow replaces guesswork with structure. Every step has a purpose, every input creates an output, and the workflow runs the same way every time without manual effort.
This is where workflow automation systems create their true value: they standardize execution while freeing your team from repetitive operational tasks.
Anatomy of a Business Automation Workflow
Every automation, no matter how simple or advanced, follows the same foundational structure. Understanding these components makes it easier to design workflows that are reliable, scalable, and aligned with your business goals.
Trigger
The event that starts the automation.
Examples: form submission, payment received, status change, date/time.
Action
What the system does automatically.
Examples: send an email, assign a task, update a CRM field.
Conditional logic
Rules that guide the workflow.
Examples: If lead score > 50, route to sales. If payment fails, send a reminder.
Outcome
The final result of the workflow is ideally something that moves the business forward.
Examples: sales follow-up completed, onboarding started, report delivered.
This structure is the backbone of every powerful automation system.
Example Workflow 1 – Sales Automation System
A strong sales workflow ensures that leads are handled consistently and fast without relying on reps to remember every step. Here’s a typical sequence:
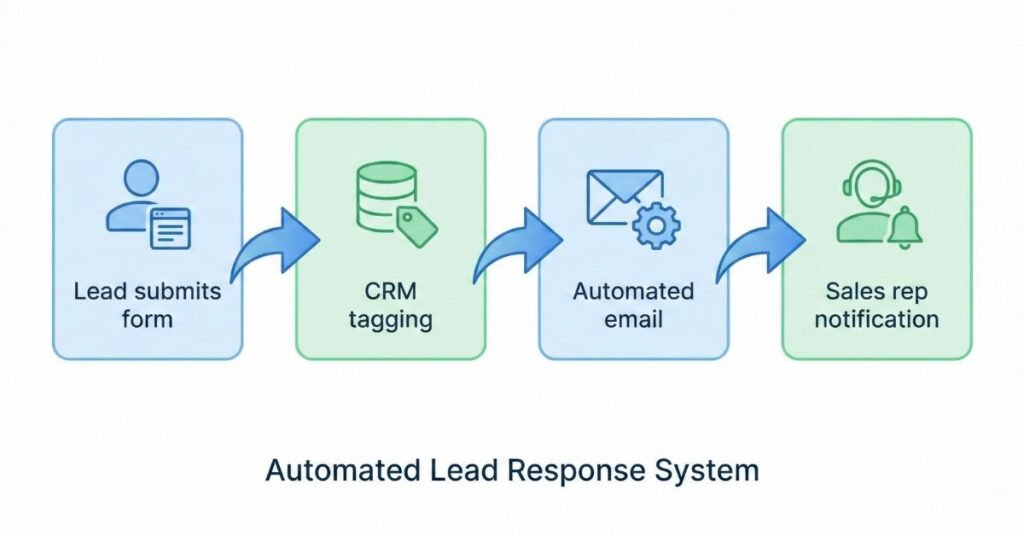
1. Lead capture
A prospect fills out a form or downloads a resource. This event becomes the trigger.
2. Tagging
The system applies labels such as lead source, interest level, or campaign.
3. Follow-up sequence
A nurturing email sequence begins automatically, delivering timely, relevant content.
4. Sales rep notification
If the lead meets the qualification criteria, a task or CRM notification is instantly created.
This ensures every lead enters a seamless journey instead of falling through cracks.
Example Workflow 2 – Client Onboarding Automation
Onboarding sets the tone for the entire client relationship. Automation ensures the experience is smooth, consistent, and fast.
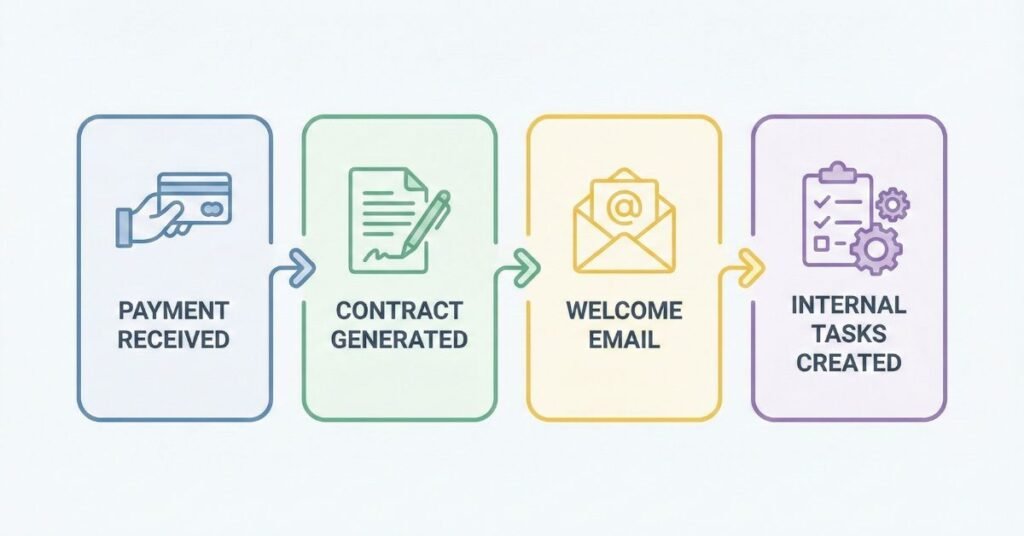
1. Payment received
A successful transaction triggers the automation.
2. Contract triggered
The system sends a prefilled contract or service agreement for signature.
3. Welcome email
The client receives an immediate, personalized message outlining next steps.
4. Task creation
Internal tasks are automatically assigned to the appropriate team members.
This eliminates the need for manual tracking and ensures clients feel supported from day one.
Example Workflow 3 – Reporting & Analytics Automation
Reporting is essential for operational clarity, but manually pulling data is time-consuming and prone to error. Automation solves this with predictable, real-time insights.
1. Data aggregation
The system pulls data from CRMs, project management tools, financial software, or support platforms.
2. KPI dashboard updates
Metrics update automatically so leadership can review performance at any moment.
3. Weekly executive report
A polished summary is generated and delivered to stakeholders, no spreadsheets required.
This is one of the most valuable examples of automation because it improves decision-making and creates measurable accountability across the business.
Core Automation Systems Every Growing Company Should Build
As your business scales, the goal is not to automate everything. It’s to automate the right things. High-performing companies focus on building a small set of foundational systems that create leverage across sales, operations, finance, and decision-making. These systems reduce friction, standardize execution, and provide the infrastructure for long-term scalability.
Below are the four automation systems that fast-growing businesses rely on to replace manual chaos with predictable, repeatable workflows.
Sales and Marketing Automation Systems
Modern growth requires consistency in how leads are captured, nurtured, and converted. Sales and marketing automation systems ensure no opportunity slips through the cracks and that customers experience timely, relevant communication.
Lead capture
Automation begins the moment a prospect interacts with your business via forms, landing pages, ads, or lead magnets.
Nurture sequences
Email journeys, SMS follow-ups, or retargeting campaigns run automatically, warming leads without additional manual labor.
CRM automation
New leads are tagged, scored, routed, and tracked without your team entering data by hand, ensuring reps focus on conversations, not admin work.
These systems are the engine behind scalable demand generation.
Operations Workflow Automation
Day-to-day operations often create the heaviest manual burden as teams grow. Operational automation for scaling companies is essential for maintaining consistency, quality, and speed across internal processes.
Task routing
Work is automatically assigned to the right team member based on rules such as availability, role, or department.
Internal notifications
Teams receive instant updates when tasks change status, deadlines approach, or dependencies shift.
Project updates
Systems keep projects moving by updating timelines, creating subtasks, and triggering alerts when milestones are reached.
This reduces operational drag and ensures nothing depends on memory, sticky notes, or scattered communication.
Financial & Administrative Automation
Finance and admin tasks might not be glamorous, but they are critical and often the most repetitive. Automating them removes unnecessary overhead and reduces costly errors.
Invoicing
Invoices are generated and sent automatically based on contracts, deliverables, or project completion.
Payment reminders
Gentle, timely reminders go out automatically, improving cash flow without uncomfortable manual chasing.
Expense tracking
Receipts sync from bank feeds or apps, categorized and ready for review, ensuring accurate reporting.
These systems stabilize financial operations and free your team from ongoing paperwork.
Reporting & Performance Automation
Insights drive growth but only if they’re accurate and accessible. Manually pulling reports is slow and error-prone. Automation fixes this with real-time, actionable data.
KPI dashboards
Metrics update automatically so leaders can see performance at a glance across sales, marketing, operations, and finance.
Data syncing
Information flows between tools, CRM, project management, and finance apps without manual exports or imports.
Forecasting
Automated models generate predictable revenue insights, resource needs, or project timelines, improving planning and decision-making.
This is where companies shift from reactive management to data-driven leadership.
Small Business Automation and Online Business Automation Strategies
Small businesses and online-first companies often feel the burden of manual work more intensely than larger organizations. With limited resources, small teams must prioritize efficiency and consistency to scale sustainably. This is where small business automation and online business automation strategies become transformative, helping founders reclaim time, reduce operational drag, and deliver a consistent customer experience without needing a large staff.
Small Business Automation Priorities
For small businesses, automation should start with foundational, high-impact processes that free up time immediately. The goal is to build leverage, not complexity.
Focus on high-impact processes
The best candidates for automation are tasks done daily or weekly: lead capture, appointment scheduling, invoicing, follow-ups, and onboarding steps. These areas absorb significant time but follow consistent patterns, making them ideal for automation.
Affordable automation stack
Small businesses don’t need enterprise systems. Modern tools offer low-cost, high-value capabilities such as automated email sequences, CRM management, task routing, and payment workflows. The key is choosing systems that integrate easily and don’t require technical expertise.
Quick wins
To build momentum, start with workflows that deliver immediate relief: automated reminders, recurring tasks, new lead notifications, and simple nurture sequences. These “quick wins” increase efficiency and build confidence to automate more complex workflows later.
When implemented correctly, small business automation becomes a strategic multiplier, allowing small teams to operate with the consistency and professionalism of much larger organizations.
Online Business Automation
Online businesses, whether selling digital products, courses, services, or memberships, rely on predictable, frictionless digital journeys. Automation is what keeps those journeys flowing smoothly at scale.
Digital funnel automation
From ad click to purchase, automated funnels ensure that prospects receive relevant content, timed follow-up, and personalized offers based on behavior. This replaces sporadic outreach with consistent, conversion-focused communication.
E-commerce workflows
Online stores benefit from automation across order processing, cart recovery, shipping notifications, and post-purchase messaging. These workflows reduce manual fulfillment tasks and increase customer satisfaction.
Payment and onboarding integration
When a customer pays, the system can automatically deliver digital products, grant course access, send onboarding emails, or create client tasks. No manual intervention required.
Effective online business automation not only improves efficiency. It also creates a seamless customer experience that builds trust, reduces friction, and increases lifetime value.
AI for Business Automation: The Intelligent Layer
Traditional automation follows rules. AI for business automation adds intelligence. It’s the difference between a workflow that executes predefined steps and one that learns, adapts, and improves over time. As companies generate more data and their operational complexity increases, AI becomes the strategic layer that elevates automation from mechanical efficiency to smart decision-making.
What Makes AI-Driven Automation Different?
AI-driven automation doesn’t just automate tasks; it enhances them with predictive logic and real-time adaptability. Instead of relying exclusively on if/then rules, AI models analyze patterns, forecast outcomes, and adjust workflows dynamically.
Predictive logic
AI anticipates what should happen next. It can detect which leads are most likely to convert, which customers might churn, or which tasks create bottlenecks before they occur.
Adaptive workflows
While rule-based automation follows instructions, AI-powered workflows change based on behavior, historical data, or contextual signals. This means processes become more personalized, accurate, and efficient the longer they run.
AI transforms automation from a static system into a responsive intelligence layer that continuously optimizes performance.
Use Cases of AI for Business Automation
AI unlocks automation possibilities that go far beyond repetitive task execution. Here are high-value use cases that create immediate impact for growing companies:
Lead scoring
AI evaluates demographic, behavioral, and engagement data to determine which leads are most likely to convert. Sales teams focus their time where it matters most.
Smart email personalization
AI tailors messaging based on customer behavior, preferences, past interactions, and predicted interests at scale.
Predictive churn alerts
AI identifies patterns that typically precede customer churn, enabling proactive outreach before revenue is lost.
AI-powered reporting insights
Instead of manually interpreting dashboards, AI highlights trends, anomalies, and actions that leaders should take. It turns raw data into recommendations.
These capabilities make automation not just faster, but smarter, driving better decisions across the entire organization.
When to Introduce AI Into Automation Systems
AI delivers enormous value, but timing matters. Introducing it too early, before your processes or data are mature, can lead to inaccurate predictions or unnecessary complexity.
Data maturity
AI performs best when you have reliable, structured data flowing consistently through your systems. Companies with automated workflows, CRM discipline, and organized repositories see the strongest results.
Volume of transactions
AI needs meaningful sample sizes to learn effectively. High lead volumes, frequent customer interactions, or large transactional datasets accelerate accuracy and impact.
In short, AI becomes a powerful accelerator once your foundational automations are in place. It’s the next evolution, not the starting point of a scalable automation strategy.

Claim your free kit to Power Your Business with AI
How to Build a Business Automation Roadmap
Building an effective automation program requires more than adding tools or automating tasks at random. You need a structured automation roadmap for growing businesses, a strategic plan that ensures every workflow you automate contributes to operational efficiency, scalability, and revenue growth.
A well-designed roadmap becomes the backbone of an automation strategy for business growth, allowing your organization to scale without chaos and empowering your team with systems that make work easier, faster, and more consistent.
Below is a proven framework used by high-performing companies to build automation systems that deliver long-term value.
Step 1 – Audit Existing Business Automation Processes
Before creating new workflows, you need clarity on what is already happening inside your business, both manually and automatically.
Identify repetitive tasks
Look for tasks performed daily or weekly, especially those that involve data entry, handoffs, follow-ups, or status updates.
Document workflows
Map out the steps for each process as it exists today. This reveals inefficiencies, complexity, and opportunities for automation.
The audit ensures you automate intentionally, not reactively.
Step 2 – Prioritize Based on Impact
Not all processes deliver equal value when automated. Prioritization ensures your team focuses on high-leverage opportunities first.
High frequency
Tasks repeated often offer the highest return on automation.
High error rate
Manual processes with inconsistent outcomes benefit greatly from automation’s reliability.
Revenue impact
Workflows tied to lead conversion, onboarding, fulfillment, or billing should move to the top of the list.
This prioritization model ensures automation supports the strategic goals of the business, not just operational convenience.
Step 3 – Map and Design the Workflow
Once priorities are clear, design the workflows with precision. Effective workflows are built, not guessed.
Flowchart planning
Visualize the journey from start to finish. Identify decision points, handoffs, and opportunities to streamline steps.
Define triggers and outcomes
Every automation must have clear starting points (triggers) and measurable results (outcomes). This clarity prevents scope creep and ensures accuracy during implementation.
Thoughtful design is what transforms single automations into scalable systems.
Step 4 – Implement, Test, Optimize
Automation is not a one-and-done project. It’s an iterative cycle of building, testing, and refining.
Beta test
Launch the workflow with a controlled set of users or scenarios to verify logic, timing, and data accuracy.
Monitor performance
Track completion rates, exceptions, and user feedback. Look for bottlenecks or unexpected behaviors.
Testing ensures each workflow is reliable before rolling it out across the organization.
Step 5 – Measure ROI
Automation delivers the strongest results when you quantify its impact. A structured ROI review shows which workflows create the most value and where future investment should go.
Time saved
Measure the reduction in manual hours to understand operational impact.
Cost per process
Compare the cost of automating a process vs. completing it manually.
Conversion improvement
Evaluate how automation influences lead response times, sales outcomes, onboarding speed, or project delivery.
This final step transforms your automation program into a measurable driver of business growth, turning systems into strategic assets.
Measuring the ROI of Business Automation Systems
Automation delivers value, but only when you measure it. The most successful companies track ROI at both the operational and financial levels, ensuring each workflow contributes to measurable growth. By evaluating performance across time, cost, and outcomes, leaders gain a clear picture of how automation strengthens efficiency, profitability, and scalability.
These metrics also validate the core benefits of business automation, turning abstract improvements into concrete performance gains.
A Simple ROI Formula You Can Use Today
Automation ROI = (Hours Saved × Hourly Value of Labor) – Cost of Automation
For example:
- Your team saves 45 hours per month
- Average blended hourly labor value = $45/hour
- Automation system cost = $400/month
ROI = (45 × $45) – $400 = $1,625 in net monthly gain
This does not include the secondary gains like faster sales response times or reduced errors, which often exceed the direct cost savings.
A Before/After Scenario That Demonstrates Transformation
Before:
A sales team manually enters new leads into the CRM, sends follow-up emails, and assigns tasks. Leads often wait 6–24 hours for a first response. Rep workloads balloon, and conversion rates stagnate at 12%.
After Automation:
Leads flow directly into the CRM, receive a personalized email within 30 seconds, and are routed instantly based on qualification signals.
Follow-up is automatic, structured, and consistent.
Result:
- Lead response time drops from 12 hours to under 1 minute
- Reps reclaim ~20 hours per month
- Conversion rate rises from 12% → 19%
- Cost-per-acquisition decreases without additional ad spend
This illustrates the emotional ROI:
less chaos, more clarity, a team that can finally breathe, and a business that grows because its systems can keep up.
Time-Based ROI Metrics
Time is the first and most universal benefit of automation. When repetitive tasks run automatically, entire workflows accelerate, and operational friction decreases.
Hours saved per month
Calculate how many hours are eliminated by automating tasks such as data entry, follow-ups, onboarding steps, or reporting.
Even small daily tasks compound into substantial monthly savings, freeing your team to focus on higher-value work.
Time-based metrics provide the clearest early signal that automation is performing well.
Financial ROI Metrics
Financial ROI confirms that automation isn’t just efficient, it’s profitable.
Cost savings
Automation reduces labor costs tied to manual tasks, errors, rework, and administrative overhead.
It also reduces the need to hire additional staff as volume increases, a major financial advantage for growing companies.
Revenue lift
Automations that improve speed, follow-up, or personalization directly contribute to higher sales conversion rates, faster onboarding, and improved retention.
This revenue impact often outweighs cost savings, making automation a growth driver, not just an efficiency tactic.
Performance KPIs
Automation strengthens performance across customer-facing, operational, and internal service workflows. Tracking these KPIs reveals the true strategic value of your systems.
Lead response time
Automated alerts, sequences, and routing dramatically reduce the delay between a lead entering your system and receiving follow-up.
Faster response times consistently correlate with higher conversion rates.
Customer retention
Automation supports retention through consistent communication, proactive check-ins, and structured onboarding, removing the inconsistencies that often cause churn.
SLA compliance
For businesses managing service-level agreements, automation ensures that tasks, updates, and deadlines occur on time, improving reliability and customer trust.
These KPIs allow leaders to measure how automation improves the quality, speed, and consistency of operations across the entire business.
Common Mistakes in Business Automation
Automation is powerful, but only when implemented correctly. Many growing businesses jump into automation without a strategy, causing more complexity instead of less. By understanding the most common mistakes, you can avoid expensive missteps and ensure your systems support scalable, predictable growth.
This section positions your brand as a trustworthy guide, someone who has seen what works, what fails, and how to implement automation with clarity and confidence.
Automating Broken Processes
One of the biggest mistakes is automating a process that doesn’t work in the first place.
If the steps are unclear, inconsistent, or no longer aligned with how the business operates, automation simply makes the inefficiency happen faster.
Instead, always optimize the workflow before automating it.
Signs of a broken process include:
- Frequent exceptions
- Confusion about responsibilities
- Steps that vary between team members
- Manual workarounds no one can explain
Automation cannot fix structural problems; it only magnifies them.
Over-Automation That Hurts Experience
More automation isn’t always better. When companies automate too much, the customer experience can feel impersonal, rigid, or robotic.
Examples include:
- Automated emails with no personalization
- Chatbots are replacing necessary human interaction
- Rigid workflows that ignore context or exceptions
Great automation enhances the experience; it doesn’t dominate it.
The goal is balance automation, the predictable, and empower humans where nuance matters.
Poor Data Integration
Automation depends on clean, connected data. When tools don’t sync or records are inconsistent, automation breaks down, creating:
- Duplicate entries
- Incorrect tags or segments
- Faulty triggers
- Inaccurate reporting
Poor data integrity leads to misrouted tasks, confusing customer communication, and flawed analysis.
Before scaling your automations, ensure your data architecture is solid. Integration is not optional; it’s foundational.
Lack of Monitoring and Governance
Once automations are live, many companies adopt a “set it and forget it” mentality. This is a critical mistake.
Without monitoring and governance, automation can drift out of alignment with business goals. Common consequences include:
- Outdated workflows that no longer match processes
- Tasks triggering incorrectly
- Delays going unnoticed
- Compliance gaps
Automation requires oversight, regular audits, clear documentation, and ongoing optimization.
High-performing companies treat automation like an evolving system, not a one-time project.
When to Consider a Business Automation Service
For many companies, early automation efforts start with strong, simple workflows, quick wins, and noticeable time savings. But as the business grows, the complexity of systems, integrations, and data flows increases. This is often the moment leaders realize they need more than tools. They need expertise.
A professional business automation service helps organizations move beyond scattered workflows and build scalable, interconnected systems that support growth. If your internal team is stretched thin or unsure where to begin, external support can provide the clarity, structure, and technical execution required to scale with confidence.
Signs Internal Resources Aren’t Enough
Many teams hit a natural ceiling with DIY automation. They can build simple automation and workflows, but more advanced systems require deeper experience.
Common signals include:
- Your team spends more time fixing automations than benefiting from them
- Everyone is unsure which workflows exist or how they work
- Tools have been added, but processes still feel manual
- Automations break frequently due to inconsistent data or unclear logic
- No one feels confident designing systems that scale beyond the short term
These challenges don’t mean your team is lacking. They simply indicate that you’ve outgrown basic tools and need a more strategic systems approach.
Complex Integrations and Scaling Challenges
As companies grow, they typically use multiple platforms for CRM, project management, finance, marketing, HR, and customer support. Getting these tools to communicate seamlessly is far more challenging than building individual automations.
You may need a business automation partner when:
- Multi-platform integrations require API work or custom routing
- Data must sync bi-directionally between systems
- You’re consolidating tech tools and need a smooth migration
- Automation logic becomes too complex for no-code builders
- You need a unified architecture rather than scattered workflows
These situations benefit from someone who understands system design, not just tool configuration.
Custom Workflow Requirements
For scaling companies, off-the-shelf templates only go so far. Your workflows reflect your business model, team structure, and customer journey. When those workflows become more advanced, you may need support developing custom logic and processes.
Examples include:
- Multi-step onboarding across different departments
- Sales workflows with advanced scoring, routing, or enrichment
- Fulfillment processes with conditional task trees
- Financial automations tied to billing cycles, SLAs, or project phases
- AI-enhanced workflows requiring training data or pattern logic
This is where Ales becomes your strategic partner to help you with business automation services. We design authoritative and scalable automated systems that directly support your business growth.
Conclusion – Automation as Growth Infrastructure
Automation isn’t a shortcut; it’s infrastructure. Just as businesses rely on financial systems, communication systems, and operational systems to function, automation becomes the underlying framework that keeps everything running predictably as you grow.
When designed intentionally, systems create clarity, consistency, and confidence. They remove the bottlenecks that slow teams down and replace reactive effort with proactive execution. This is the difference between a business that strains under growth and one that scales smoothly.
Smart business automation enables sustainable scaling by ensuring your operations can support higher volume without sacrificing quality, speed, or customer experience. It gives leaders better visibility, teams more leverage, and customers a better journey every time.
If you’re evaluating your next stage of growth, now is the ideal moment to step back and audit your current workflows. Identify what’s working, what’s breaking, and where automation can create immediate impact. The sooner you build these foundations, the more resilient and scalable your business becomes.